As Doctors we write about evidence- based facts and with that in mind select products we believe to be the best for our readers. Thelifestylecure.com is a participant of the amazon associates program and we may earn a very small commission from qualifying purchases at no extra cost to you.
How much information do you have on metformin? Do you know what metformin may or may not work in the human body? How about how long it takes to reach its full effect? Or the difference between metformin and metformin extended release? Note that most people have these exact same questions as well, especially once they are told to start taking it. Metformin is often the first line of defense against rising blood sugar levels. And that’s because of its extremely safe and effective drug profile. Now that does not mean it doesn’t have side effects (it does) nor does it mean that it will lower your blood sugar levels immediately (it won’t). What it does mean is that Metformin is worth looking into if you have any of the following: Newly Diagnosed Diabetes, Type 2 Diabetes, Insulin Resistance, and/or Prediabetes.
Understanding how metformin can work for you and your health could be the difference between well controlled and uncontrolled diabetes.
Table of Contents
Types of Metformin
There are many different types of metformin and they are differentiated by their names. Metformin can be available in a generic tablet form that is ready for immediate release, referred to as glucophage. It is also available in an extended-release tablet form referred to as glumetza or fortamet. While oral solutions are called riomet (immediate release) and riomet ER (extended release).
Metformin extended release (ER) was recalled (discontinued) in many places around the globe including both in the United States and in Europe as of this year (2020). The reason behind the recall of several brands of Metformin ER was because of higher than normal levels of NMDA within them.
When to Take Metformin
Metformin usually takes a few days to perhaps a week to develop its full effect. In that time and even after it’s good to decide a time that works best for you.
From a healthcare professional’s point of view, most recommend that you take metformin during suppertime. Or with your evening meal atleast. This is to avoid side effects like nausea/vomiting. However, some have found that they actually benefit more when taking metformin at bedtime instead. This is because when they wake up the following morning, their blood sugar levels are even lower. This option may work for those who struggle with morning hyperglycemia (high blood sugar).
How Does Metformin Work in the Body?
It’s imperative to discuss how metformin works in the body exactly.
Why? Because by knowing this information, you gain an understanding of how it affects your body every time you take it.
Metformin has several different ways that it can work to bring down your blood sugar levels. And all are equally important as they are the reasons behind why metformin is the recommended treatment for diabetes and related conditions.
1. Decreasing sugar absorption and sugar utilization in the intestine
This is one of the most important ways that metformin can work in the body. Now normally whenever we eat sugar it enters our digestive tract where it is processed. Approximately 70% of a metformin dose is absorbed in our intestine (into the bloodstream), while the rest goes to our colon and is eventually excreted.
But metformin actually reduces this exact mechanism of sugar absorption from taking place. Meaning less sugar is now in the blood resulting in LESS hyperglycemia (high blood sugar)!
Metformin also promotes GLP-1 (hormone) secretion that allows for more glucose utilization within the intestine. Which means that metformin USES more glucose instead of STORING it.
2. Lowers the production of sugar from the liver
There are two ways that we can find sugar in our body. One way is to eat sugar (like carbohydrates) and the other is for our liver to produce it. Metformin effectively reduces the second action from taking place.
3. Improves muscle insulin sensitivity
As time proceeds, insulin resistance continues to worsen unless permanent lifestyle changes are adopted. However, if those lifestyle changes are unsuccessful then metformin can be started. With time, insulin sensitivity will then increase through several different mechanisms. One is improved glycogen synthesis, another is with an increase in GLUT transporters, and finally through increased tyrosine kinase receptor activity.
How Does Metformin Work for Weight Loss?
Whether or not metformin can cause weight loss is a common question most doctors are asked about.
And researchers have proven as much to be true as well! Though many do not know the exact mechanism of action by way that weight loss occurs, many theories exist. One such theory centers around how metformin causes a decrease in appetite and another about how it causes a redistribution of fat cells.
The largest study done till date to show how weight loss occurs as a result of metformin was the called Diabetes Prevention Study (DPP).
The results were remarkable because not only did the participants who took metformin regularly and consistently lose weight fast but maintained that weight loss for 10 years afterwards as well!
The amount of weight loss achieved varied depending upon HOW adherent participants were to metformin. The ones who were extremely adherent lost an average of 3.5% in body mass and had a noticeable waist reduction as well.
One of the biggest takeaway from DPP were the participants. They were all at high risk of getting type 2 diabetes, meaning they had high insulin resistance and/or prediabetes. And once they were started on metformin, their incidence of diabetes decreased by over 30% during a 3 year period!
Though the exact mechanism by which weight loss occurs due to metformin use is not clearly understood, many pathways have been suggested.
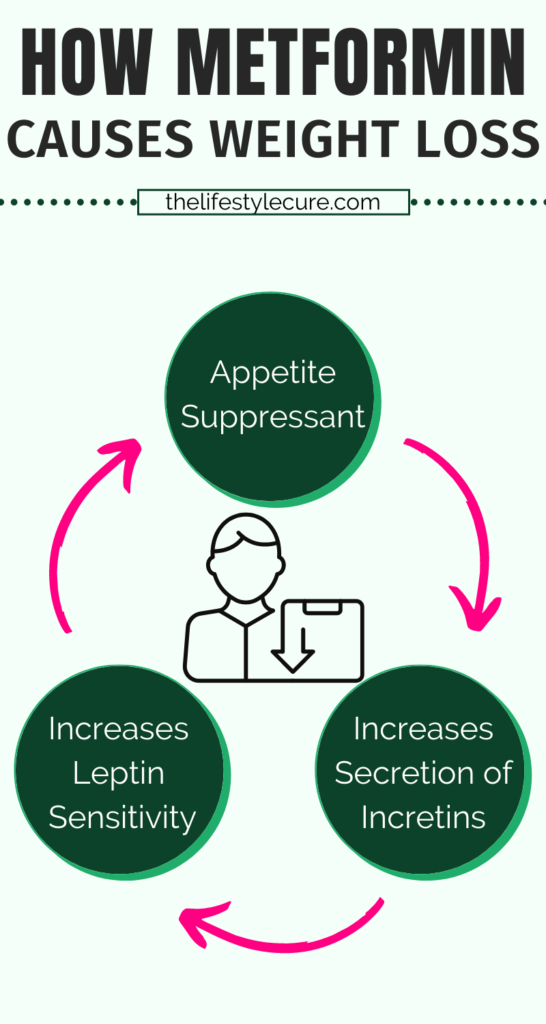
One pathway is how metformin acts as an appetite suppressant by increasing lactate production after a meal. While another is how it increases leptin sensitivity in the hypothalamus. And finally another states that metformin increases secretion of incretins (which in turn help regulate insulin secretion).
How Does Metformin Work for Prediabetes and Insulin Resistance?
It is now being reported that many doctors have started to prescribe metformin for prediabetes or those with suspected insulin resistance.
Both conditions, prediabetes and insulin resistance, can be treated with metformin effectively but it is important to treat the cause instead of simply the symptoms. That’s why changing dietary patterns, adopting more physical activity throughout the day, targeting stress levels and treating any hormonal imbalances naturally should be made a priority first.
How Does Metformin Work for PCOS/Pregnancy?
Before we discuss how metformin can affect PCOS, it’s important to see how it can affect you if you are menstruating, pregnant and/or breastfeeding.
Metformin can cause changes to the menstrual cycle, and thereby increase the chance of becoming pregnant. Talk to your doctor about birth control if this may be of concern.
If you are pregnant and/or lactating then you will need to discuss with your doctor to find out what options are available for you. Though it is safe to take metformin during pregnancy or when breastfeeding, some doctors may have you switch to insulin during the pregnancy and then switch back to metformin postpartum. But that is discussion to have with your primary care physician or OBGYN.
Also, minimal amounts of metformin can pass through the breast milk but no adverse effects have been found. More research is still being conducted in regards to this issue. In the meantime, consult with your doctor to see what options you may have.
Now, Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) is a disease seen in reproductive women characterized by the presence of hormonal imbalance that results in:
- Ovaries with multiple small cystic follicles
- Increased male hormones resulting in hirsutism (increased facial and body hair)
- Absent or irregular periods resulting in infertility
Metformin can help PCOS symptoms by way of not only reducing insulin resistance (which is generally high in females with PCOS) but also by increasing ovulation resulting in improved fertility. Which is exactly why it is considered to be one of the main drugs in treating PCOS.
Infertility due to PCOS is generally treated with clomiphene citrate (clomid) but for those who may be resistant to its action use metformin in place of it. Metformin can also be used in conjunction with clomid to attenuate its effects and is oftenly done so.
Preliminary trials even show that metformin plus clomid is better at achieving ovulation induction than just clomid alone!
Be sure to know there also instances when you should NOT take metformin when you PCOS as well:
Pros of Taking Metformin
There are several reasons why taking metformin may be beneficial for someone. For one, it is the number one preferred method of treatment for someone newly diagnosed with type II diabetes. Even for those with prediabetes, it’s being considered as a good option too.
Number two is that it doesn’t increase your weight. In fact many patients report having experienced weight loss while on metformin and now there are studies to support this as well. It is an excellent choice for candidates who are overweight or obese.
It is thought to play a role in the reversal of the consequences of aging as well.
And lastly metformin is thought to be cardioprotective because it doesn’t put any extra strain on the heart.
But beyond all these things, metformin is now being seen as an even more powerful drug. It is now being examined into treating obesity related diseases as well. Such as obstructive sleep apnea, hepatitis steatosis, and osteoarthritis!
So in summary, the factors in favor of taking metformin are the following:
- Safe drug profile – which is why it is the recommended treatment for diabetes
- Weight loss – does not cause any weight gain unlike other diabetic medications, like sulfonylureas and insulin.
- Cardioprotective – protects the heart instead of adding strain to it
- Anti-aging – reverses metabolic derangement responsible for the aging process
- For possible treatment in obesity’s sequelae
Cons of Taking Metformin
One of the cons people feel is surrounding the use of alcohol and metformin at the same time. It is recommended to limit the amount of alcohol that you consume while taking metformin to avoid the serious condition known as lactic acidosis.
Side Effects of Metformin
Usually metformin does not have any serious side effects commonly associated with it unlike other medications for treating insulin resistance, prediabetes or type II diabetes. Because it has a safer profile than others, it is generally recommended as the first line of treatment for diabetes. Meaning metformin is the first drug that is given to manage blood sugar levels once diagnosis has been confirmed.
However, there are common side effects seen when your body is first adjusting to metformin, such as nausea, vomiting, upset stomach, bloating, gas, tiredness, low B12 levels, or a metallic taste in the mouth.
If symptoms persist or specifically have an upset stomach for longer than a week to couple weeks, it’s important to go to your doctor immediately. This may be a sign of lactic acidosis or something more serious.
Diarrhea is also seen initially when starting metformin but it subsides within a couple weeks. If the diarrhea is intolerable then metformin extended release (ER) can be taken in place of its immediate release form.
Metformin ER can avoid side effects like diarrhea from occurring because it is released slowly into your system over hours, circumventing all of its effects from taking place immediately.
However, due to the recent developments of recalls occurring of metformin ER, this may not be feasible as of right now.
Allergic reactions to metformin are extremely rare but go to the hospital immediately if you develop any symptoms of allergy. Symptoms such as difficulty in breathing, persistent dizziness, swelling of face, throat etc.
Metformin and Hypoglycemia
Can metformin cause low blood sugar? Generally speaking, metformin does not cause low blood sugar normally. However, when combined with other diabetic medications such as sulphonylureas or insulin, it can cause hypoglycemia (low blood sugar).
Signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia include the following:
- Sweating
- Confusion
- Trembling/Shaky
- Difficulty concentrating
- Extreme hunger
- Fatigue
- Irritability
- Anxious/Nervous
- Increased heart rate (fast beating heart)
- Lightheadedness
Those who are at an increased risk of severe hypoglycemia are the elderly (above the age of 65), anyone in a hypoxic or dehydrated state, after heavy alcohol use, those who have endured stress due to infection, surgery or trauma, and anyone malnourished or debilitated. They should be aware of any of the warning signs of hypoglycemia that are listed above.
Who Should and Should Not Take Metformin
People who should take metformin are those who have not been able to control their type II diabetes with lifestyle management alone despite several attempts. Others include people diagnosed with polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS). As discussed above, metformin can help PCOS by increasing insulin sensitivity and regulating hormonal imbalance.
For people with prediabetes and insulin resistance who have been unsuccessful in regulating their blood sugar levels with diet and exercise alone, a low dose of metformin may be the answer they need as well.
People who should NOT take metformin are those with the following conditions:
- Kidney Disease
- Intolerance or hypersensitivity to metformin
- Congestive heart failure (CHF)
- Diabetic Coma
- Abnormal creatinine clearance resulting from MI, shock or septicemia
Also people should alert their healthcare professional and/or team before undergoing surgery or certain medical procedures that involve the use of dyes. Metformin may need to be discontinued for a short period before, during, and/or after such events.
Metformin and Other Medications
Make sure to beware of any interactions between metformin and other common medications. Ask your pharmacist and/or doctor to go over any possible interactions before beginning metformin. You should be advised on what to expect while taking more than 1 medication at a time.
Your metformin dose may need to be adjusted when coupled with any of the following meds:
- Diuretics ie. furosemide
- Steroids ie. prednisone
- Certain types of medications used to treat high blood pressure or cardiac disease
- Certain types of hormones ie. estrogen, testosterone
- Insulin and other medications used specifically for type II diabetes
Always keep in mind that all information is for educational purposes. You are still required to go see your doctor before beginning or stopping any medication.
Only they will provide you with the best advice because it will be tailored to your needs. This includes how well metformin may or may not work for you.
Summary
If you are interested in lowering your blood sugar and reversing your diabetes by losing weight, then be sure to check out our book SMART & Skinny Habits. We designed this program to help diabetics not only lose weight but REVERSE their diabetic symptoms.
Please click on this link for more information on Smart & Skinny Habits created by Dr. Naveen Gupta & Dr. Tina Gupta. Thank you!